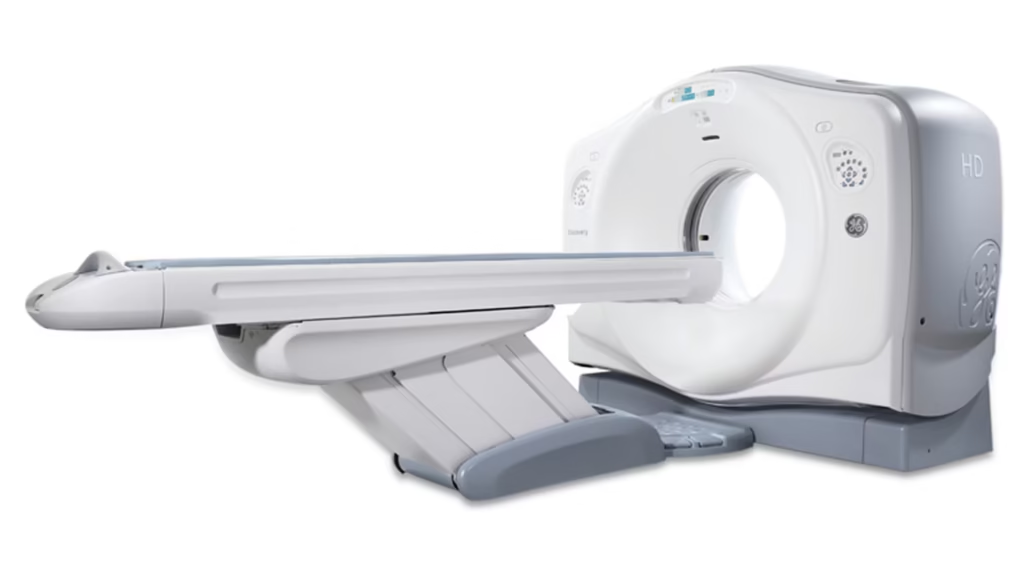
Let's Talk Now
Ready to enhance your medical imaging capabilities? Our team of experts is here to provide you with tailored solutions and support. Contact us today to start the conversation.
Head Office Address
1, Sami St., Tavanir Shomali St., Vanak Sq.. Tehran, 14375-53484, Iran
Email Address
Info@TPPGE.net
Telephone
+98 21 42681